Understanding the link between nutrition and mental health is becoming essential as more people experience stress, anxiety, mood disorders, and lifestyle-related emotional struggles. Your brain depends on the nutrients you eat every day, and even small nutritional deficiencies can influence how you feel, think, and respond to situations. When nutrition improves, mental stability, emotional clarity, and resilience also begin to strengthen. This article explains in depth how food affects the brain, why nutritional balance is critical during addiction recovery, and how you can use scientifically backed nutritional strategies to enhance psychological well-being.
Nutrition and Mental Health
The connection between nutrition and mental health is one of the most compelling areas of modern psychology and neuroscience. Research consistently shows that the quality of your diet affects mood, stress tolerance, sleep, motivation, focus, and even your ability to regulate emotions. A nutrient-rich diet supports stable brain chemistry, while poor nutrition can contribute to irritability, anxiety, depression, and behavioural challenges commonly seen in both adults and teenagers.
At the beginning of this discussion, it is important to highlight that Aarogya Sewa Samiti has long emphasized the importance of integrating nutrition and mental health strategies into recovery programs. Their approach acknowledges that healing requires not just therapy and medication but also a strong nutritional foundation that brings biochemical balance back to the brain. When individuals struggling with addiction, emotional instability, or psychological distress begin to nourish their bodies appropriately, they experience clearer thinking, calmer emotional states, and greater stability.
Food is not just energy—it is biochemical information. What you eat influences hormones, neurotransmitters, and inflammation levels, all of which directly affect mental health. This is why the link between nutrition and mental health is now considered essential for recovery and long-term emotional resilience.
How Nutrition Supports the Brain: A Science-Backed Breakdown
Below are the key ways nutrition and mental health interact at the biological level:
1. Nutrition Regulates Neurotransmitters
Brain chemicals such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA are deeply influenced by food. Serotonin (the “happiness chemical”) is produced from tryptophan found in foods like eggs, nuts, seeds, and dairy. A diet lacking in these nutrients may lead to low mood, sadness, irritability, or sleep problems.
2. Nutrition Influences Stress Hormones
Foods rich in magnesium, omega-3 fatty acids, and B-vitamins help regulate cortisol—the body’s primary stress hormone. When cortisol remains too high due to poor diet or chronic stress, anxiety and mood swings increase.
3. Nutrition Builds a Healthy Gut–Brain Connection
The gut produces nearly 95% of the body’s serotonin. Healthy gut bacteria also support emotional regulation, which is why probiotics and fiber-rich foods help improve nutrition and mental health outcomes.
4. Nutrition Reduces Inflammation
High-sugar and processed foods increase inflammation, which is linked to depression and cognitive fog. Anti-inflammatory foods like vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish improve focus, mood, and mental clarity.
The Role of Nutrition and Mental Health in Addiction Recovery
Addiction severely depletes nutrients such as B vitamins, magnesium, zinc, and essential fatty acids. These deficiencies contribute to:
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Depression
- Cravings
- Fatigue
- Poor impulse control
Replenishing these nutrients is essential for restoring balanced brain chemistry. This makes nutrition and mental health a crucial pillar of rehabilitation. When clients receive a structured diet plan rich in essential nutrients, they recover faster, sleep better, experience fewer mood swings, and develop greater emotional stability.
Nutrition is not an “extra”—it is a core therapeutic component.
Foods That Support Mental Health and Emotional Stability
Below is a comprehensive guide to foods scientifically shown to strengthen nutrition and mental health outcomes.
1. Omega-3 Rich Foods
Fish, flaxseeds, walnuts
→ Reduce depression, enhance brain flexibility
2. Whole Grains
Oats, brown rice, quinoa
→ Support serotonin production and stable energy levels
3. Leafy Greens
Spinach, kale, methi
→ High in folate and magnesium, reduces anxiety
4. Probiotic-Rich Foods
Curd, buttermilk, fermented foods
→ Improve gut–brain communication
5. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds
→ Provide essential fatty acids for brain function
6. Lean Proteins
Paneer, dal, eggs, chicken
→ Boost neurotransmitter production
7. Colourful Fruits and Vegetables
Berries, carrots, beets, oranges
→ High antioxidants reduce mental fatigue
8. Dark Chocolate (moderate)
→ Enhances mood and reduces stress hormones
These foods build long-term emotional resilience, underscoring the close connection between nutrition and mental health.

How Poor Nutrition Damages Mental Health
Understanding the negative effects of bad eating habits is essential:
1. High Sugar Intake
→ Causes rapid spikes and drops in energy, contributing to irritability and anxiety.
2. Processed Foods
→ Increase inflammation linked to depression.
3. Skipping Meals
→ Interferes with mood regulation and leads to emotional instability.
4. Low-Protein Diets
→ Reduce neurotransmitter production, affecting mental balance.
5. Excessive Caffeine
→ Raises anxiety and disrupts sleep, worsening mood.
These patterns disrupt the delicate connection between nutrition and mental health, making emotional stability harder to maintain.
10 Lifestyle Strategies to Strengthen Nutrition and Mental Health
These evidence-based practices help improve psychological well-being:
1. Eat Balanced Meals Regularly
Avoid skipping meals; maintain stable blood sugar.
2. Prioritize Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Supports mood regulation and cognitive sharpness.
3. Add Probiotics Daily
Strengthens gut health and emotional stability.
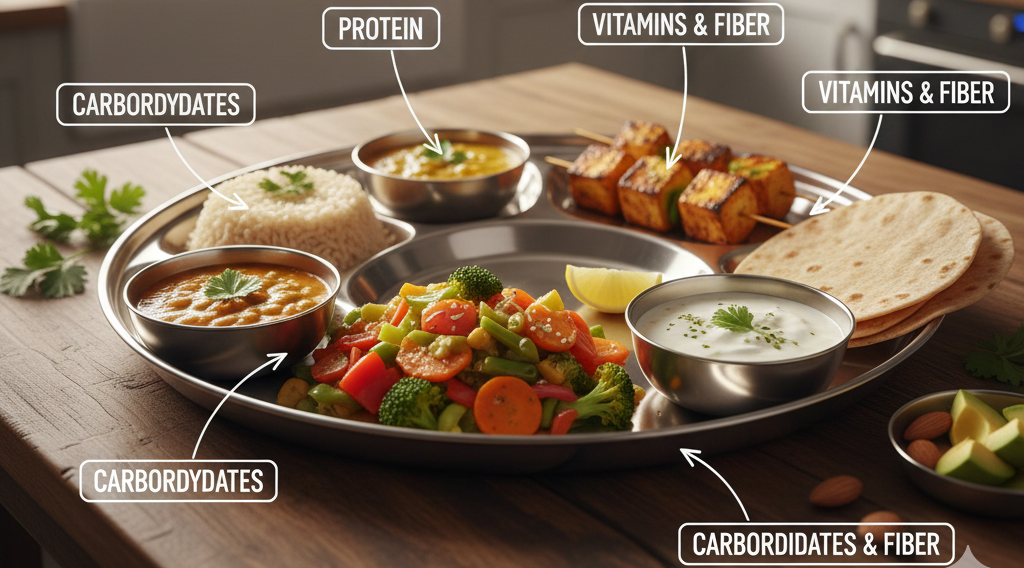
4. Use the Plate Method
½ vegetables, ¼ protein, ¼ whole grains.
5. Reduce Sugar Slowly
Avoid sudden withdrawal; reduce gradually.
6. Stay Hydrated
Even mild dehydration worsens anxiety.
7. Include Evening Magnesium Sources
Helps with sleep and relaxation.
8. Plan Weekly Meal Prep
Reduces impulsive eating choices.
9. Track Your Mood and Meals
Helps identify patterns affecting emotional well-being.
10. Combine Nutrition With Therapy
A powerful way to enhance recovery and cognitive strength.
These strategies help maintain a strong link between nutrition and mental health every day.
Conclusion
Nutrition plays a key role in strengthening emotional resilience and supporting long-term mental well-being. A balanced diet helps stabilise mood, sharpen focus, and improve overall brain function. When individuals nourish their bodies well, they build a stronger foundation for healthier thinking and emotional stability.
For those recovering from addiction or emotional challenges, prioritising nutrition is essential. Modern rehab centres now combine therapy with structured diet plans for better results. Aarogya Sewa Samiti, one of the best rehab centres in Dehradun, follows this integrated approach to support meaningful and lasting recovery.
