Addiction is more than just a physical dependence on substances like drugs or alcohol—it affects mental, emotional, and social well-being. Overcoming addiction requires not just willpower, but structured therapeutic approaches that address both the mind and behaviour. One of the most effective methods in this area is Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT). This therapy has become a cornerstone for individuals seeking mental health support and long-term recovery from substance use disorders. At Aarogya Sewa Samiti, we incorporate CBT as part of our comprehensive programs to help individuals rebuild their lives and achieve lasting recovery.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Cognitive Behavioural Therapy?
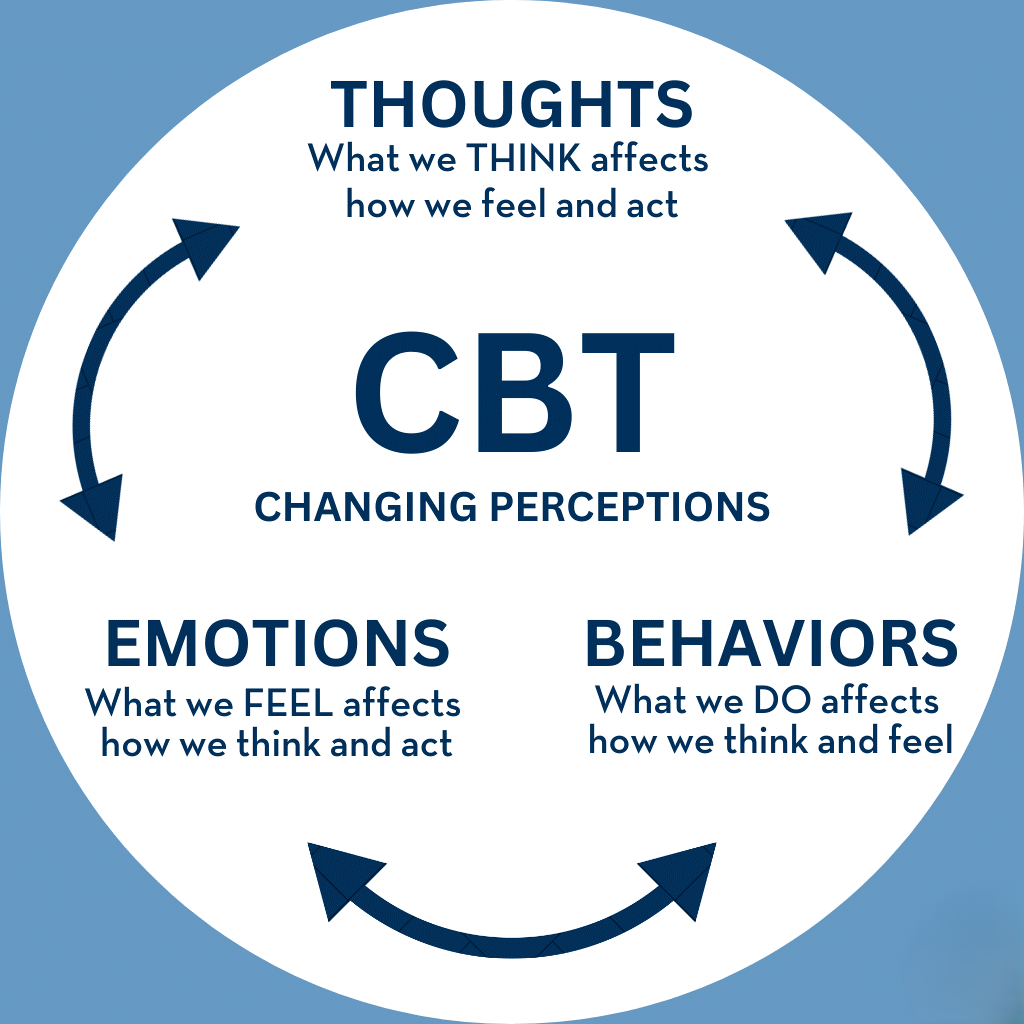
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns, beliefs, and behaviours. It operates on the principle that our thoughts influence our feelings and actions. For someone struggling with addiction, these thought patterns often contribute to substance use. For example, feelings of hopelessness, anxiety, or stress can lead a person to seek comfort in drugs or alcohol. CBT helps individuals recognize these triggers and develop healthier coping strategies.
Unlike therapies that primarily focus on discussing past experiences, CBT is solution-focused and practical. It empowers individuals to address their present challenges, manage cravings, and prevent relapse. By teaching coping skills, stress management, and problem-solving techniques, Cognitive Behavioural Therapy provides tools that are crucial for sustainable recovery.
How Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Works
The process of Cognitive Behavioural Therapy involves several key steps that work together to create meaningful behavioural change:
Identifying Negative Thoughts: The first step in CBT is to help individuals recognize destructive thought patterns. In addiction, these might include thoughts like “I can’t cope without drugs” or “One drink won’t hurt.” Identifying these thoughts is critical because they often drive compulsive behaviour.
Challenging and Restructuring Thoughts: Once negative thoughts are identified, CBT helps individuals question their accuracy and replace them with positive, realistic alternatives. For example, “I can handle stress through exercise or meditation instead of drugs.” This restructuring reduces the emotional power of harmful thoughts.
Behavioural Interventions: CBT also addresses the actions resulting from negative thoughts. This may include creating avoidance strategies for triggers, practicing refusal skills, or developing healthier routines. By changing behaviour, individuals gradually reinforce positive thought patterns.
Skill Building for Relapse Prevention: A major component of Cognitive Behavioural Therapy is teaching skills to prevent relapse. This includes managing cravings, coping with stress, and developing social support systems. These skills empower individuals to maintain sobriety long after the therapy sessions end.
Benefits of Cognitive Behavioural Therapy in Addiction Recovery
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy offers multiple advantages for those struggling with addiction:
Reduces Cravings and Risk of Relapse: By identifying triggers and developing coping mechanisms, CBT significantly lowers the risk of relapse.
Improves Emotional Regulation: Many people with substance use disorders struggle with emotional instability. CBT helps regulate emotions like anger, anxiety, and depression.
Enhances Self-Awareness: Individuals gain a better understanding of their thoughts, feelings, and behaviours, leading to more mindful decision-making.
Strengthens Coping Strategies: CBT equips individuals with practical tools to deal with stress, peer pressure, and high-risk situations without turning to substances.
Supports Overall Mental Health: Beyond addiction, CBT helps treat co-occurring conditions like depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), which often accompany substance abuse.
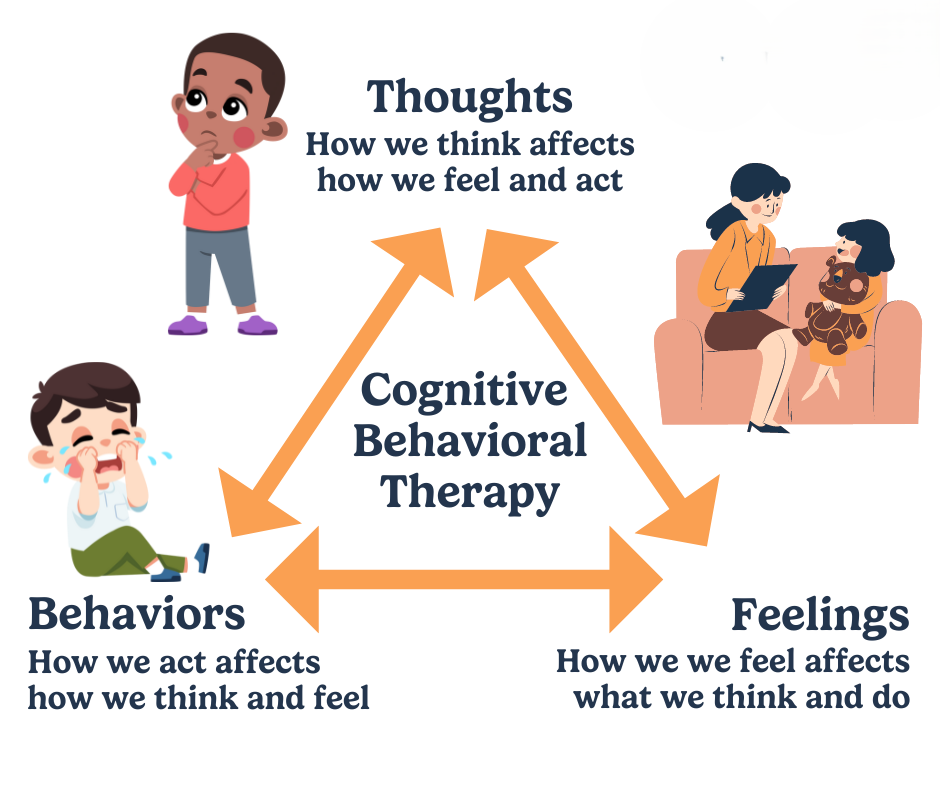
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy and Mental Health
Addiction rarely exists in isolation. Mental health issues frequently coexist with substance use disorders, creating a cycle that is difficult to break without professional intervention. Cognitive Behavioural Therapy addresses both sides of this equation: it not only targets addictive behaviours but also the underlying mental health challenges.
For example, an individual struggling with anxiety might use alcohol as a temporary relief mechanism. CBT helps them identify this connection and teaches healthier alternatives for coping with anxiety, such as mindfulness exercises, journaling, or relaxation techniques. Over time, the therapy reduces both the psychological need for substances and the likelihood of relapse.
Practical Techniques Used in CBT for Addiction
Several techniques make Cognitive Behavioural Therapy particularly effective for addiction recovery:
Cognitive Restructuring: Helps individuals identify irrational or harmful thoughts and replace them with constructive ones.
Behavioural Experiments: Encourages individuals to test new behaviours in real-life situations to reinforce positive change.
Exposure Therapy: Gradually exposes individuals to triggers in a controlled setting, reducing fear and anxiety associated with those triggers.
Mindfulness-Based CBT: Combines mindfulness practices with traditional CBT to improve emotional regulation and present-moment awareness.
Problem-Solving Skills Training: Teaches practical skills to tackle daily challenges without resorting to substances.
These techniques are usually customized based on the individual’s specific needs, addiction severity, and co-occurring mental health conditions.
The Role of CBT in Group and Individual Therapy
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy can be delivered in both individual and group settings.
Individual CBT: Provides one-on-one sessions with a therapist, allowing for personalized guidance, deep exploration of thought patterns, and tailored interventions.
Group CBT: Offers peer support, shared experiences, and collaborative learning. Participants gain motivation from seeing others overcome similar struggles and practice social skills in a supportive environment.
Both formats are effective, and many rehabilitation programs combine them to maximize outcomes.
Combining CBT with Other Treatments
While Cognitive Behavioural Therapy is highly effective on its own, it often works best when combined with other treatments:
Medical Detox: Safely manages withdrawal symptoms before CBT begins.
Medication-Assisted Treatment: Helps address cravings or co-occurring mental health conditions.
Family Therapy: Strengthens support systems and improves communication with loved ones.
Lifestyle Interventions: Encourages physical activity, nutrition, and mindfulness to enhance overall well-being.
This holistic approach ensures that individuals receive comprehensive care addressing both body and mind.
 Signs CBT Can Help
Signs CBT Can Help
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy may be particularly beneficial for individuals who:
Experience frequent cravings or compulsive substance use
Struggle with depression, anxiety, or stress-related triggers
Have difficulty managing emotions or responding to high-risk situations
Have relapsed multiple times and need structured relapse prevention strategies
Want to develop long-term coping skills for sustained recovery
By recognizing these signs, individuals can seek timely intervention and improve their chances of successful recovery.
Why Choose CBT for Addiction Recovery?
There are several reasons why Cognitive Behavioural Therapy is widely recommended in addiction treatment:
Evidence-Based: Numerous studies support its effectiveness in reducing substance use and preventing relapse.
Structured and Goal-Oriented: Focuses on measurable outcomes and practical skills.
Empowering: Gives individuals tools to take control of their thoughts, emotions, and actions.
Adaptable: Can be tailored to any age group, type of addiction, or mental health condition.
Long-Term Benefits: Skills learned in CBT continue to benefit individuals well beyond the treatment period.
CBT doesn’t just help people quit substances—it equips them to rebuild their lives, improve relationships, and regain self-confidence.
Challenges and Considerations
While Cognitive Behavioural Therapy is highly effective, it requires commitment and active participation. Recovery is a gradual process, and individuals may encounter challenges such as:
Difficulty confronting painful thoughts or past experiences
Resistance to change or scepticism about therapy
Occasional setbacks or relapses, which are part of the recovery journey
Professional guidance, a strong support system, and consistent practice of CBT techniques are essential to overcome these obstacles.
Supporting Recovery Beyond Therapy
Recovery doesn’t end when therapy sessions conclude. CBT encourages individuals to maintain their progress by integrating learned skills into daily life. This includes:
Practicing mindfulness or relaxation techniques regularly
Identifying early warning signs of relapse
Maintaining healthy routines and social connections
Continuing follow-up sessions or booster therapy when needed
By reinforcing positive habits, individuals can sustain long-term recovery and improve overall mental health.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy is a proven, structured approach that addresses both the psychological and behavioural aspects of addiction. It equips individuals with the tools to manage triggers, regulate emotions, and build a life free from substance dependence. By combining CBT with medical care, counseling, and supportive environments, recovery becomes not only achievable but sustainable.
For those seeking professional assistance in overcoming addiction, services like Best Rehab Centre in Dehradun integrate Cognitive Behavioural Therapy into comprehensive treatment programs, providing the guidance, care, and support necessary for lasting recovery.